The Architecture of Spectacle: A Multidisciplinary Analysis of the Psychology, Sociology, and Ontological Impact of Reality Television


In today's interconnected world, communication methods have evolved significantly, shaping the way we interact and collaborate. This article explores the contrasting dynamics of synchronous and asynchronous communication, delving into their characteristics, benefits, and applications across various disciplines. By understanding the nuances of these communication methods, individuals can navigate digital interactions more effectively and enhance productivity, collaboration, and well-being.
 |
| Communication methods have evolved significantly (📷 CC/MIT) |
Communication lies at the heart of human interaction, facilitating the exchange of ideas, information, and emotions. In the digital age, advancements in technology have revolutionised the way we communicate, offering a myriad of methods to connect with others. Two primary modes of communication have emerged: synchronous and asynchronous. While synchronous communication occurs in real-time, allowing for immediate interaction, asynchronous communication enables individuals to communicate without the need for simultaneous participation. Understanding the differences between these modes is essential for navigating the complexities of modern communication.
Synchronous communication involves interactions that occur in real-time, where participants engage simultaneously. Examples include face-to-face conversations, phone calls, and live video conferences. This mode of communication facilitates immediate feedback, fosters spontaneity, and promotes a sense of connection among participants. In fields such as emergency response, healthcare, and crisis management, synchronous communication is vital for swift decision-making and coordination.
On the other hand, asynchronous communication allows individuals to communicate without requiring immediate responses. Email, text messaging, and discussion forums are common examples of asynchronous communication channels. This mode offers flexibility, enabling participants to engage at their own pace and convenience. Asynchronous communication is particularly beneficial for distributed teams, remote work settings, and collaborative projects spanning different time zones.
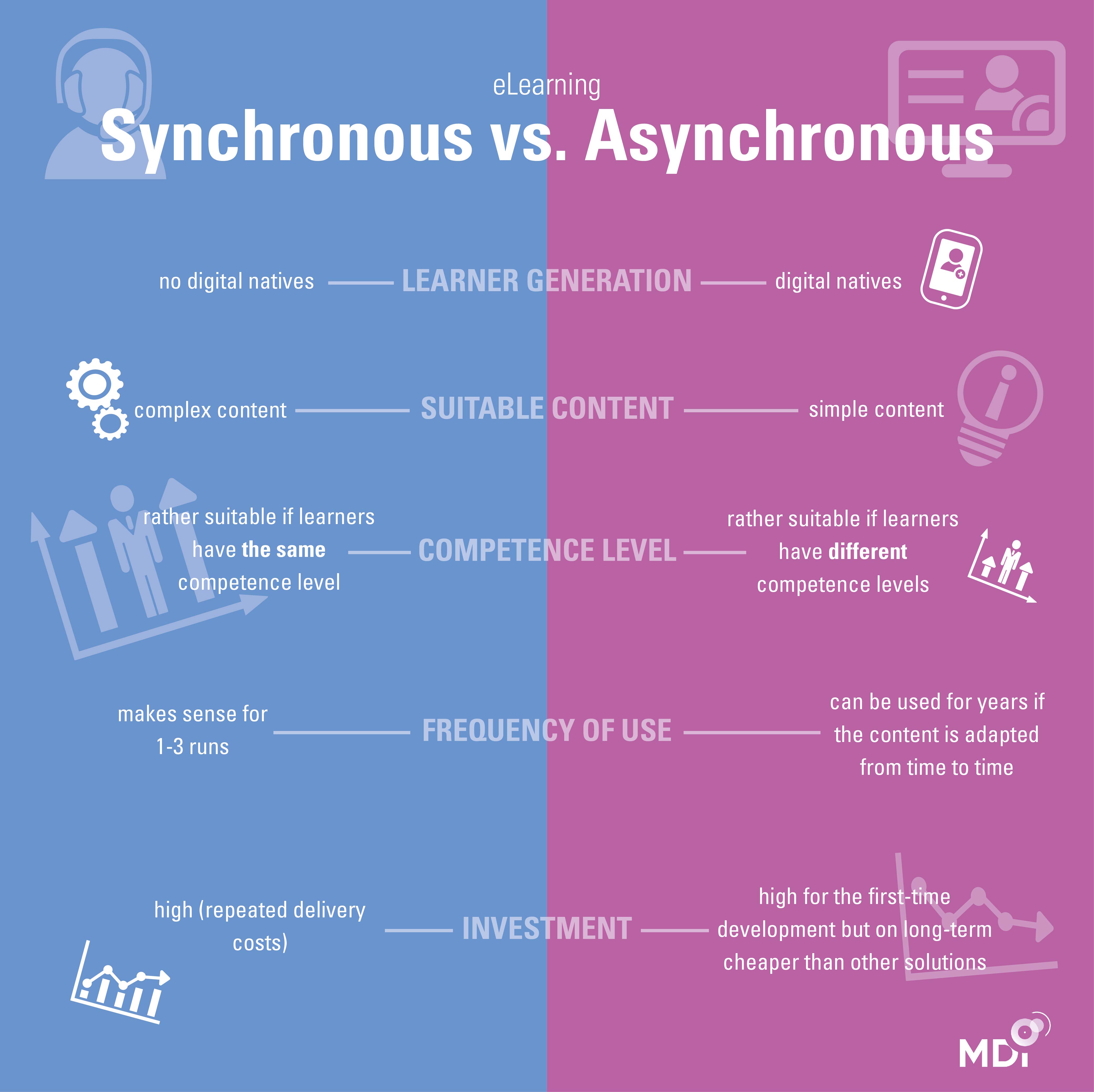 |
| Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Communication in eLearning (📷 mdi-training) |
Both synchronous and asynchronous communication methods offer unique benefits and challenges. Synchronous communication fosters real-time engagement and spontaneity, making it ideal for quick decision-making and brainstorming sessions. However, it may also lead to interruptions and difficulties in coordinating schedules. In contrast, asynchronous communication promotes flexibility and allows individuals to process information at their own pace. Yet, it can result in delays in responses and challenges in maintaining momentum.
The choice between synchronous and asynchronous communication depends on various factors, including context, objectives, and preferences. In education, synchronous communication supports live lectures, interactive discussions, and virtual classrooms, enhancing student engagement and collaboration. Conversely, asynchronous communication facilitates self-paced learning, enabling students to access course materials and participate in discussions asynchronously.
 |
| The choice between synchronous and asynchronous communication depends on various factors (📷 marketing91) |
Synchronous and asynchronous communication methods each offer distinct advantages and considerations. By understanding their characteristics and applications across disciplines, individuals can leverage these modes of communication to enhance productivity, collaboration, and connection in both personal and professional contexts. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, mastering both synchronous and asynchronous communication skills is essential for effective communication in the modern world.
⭐⭐⭐
*AI assisted
Comments