The Architecture of Spectacle: A Multidisciplinary Analysis of the Psychology, Sociology, and Ontological Impact of Reality Television


In the ever-expanding digital landscape, where algorithms govern our online experiences, the concept of algorithmic literacy has become increasingly crucial. Algorithmic literacy refers to the ability to understand, interpret, and critically engage with the algorithms that shape our digital interactions. From social media feeds to search engine results, algorithms play a significant role in curating the content we consume, influencing our perceptions, decisions, and behaviours.
 |
| The concept of algorithmic literacy has become increasingly crucial. (📷 flickr) |
At its core, algorithmic literacy involves grasping the fundamental principles behind algorithms. These complex mathematical formulas are designed to process data, identify patterns, and generate outputs based on predefined criteria. By comprehending how algorithms work and the factors they consider, individuals can better comprehend the information presented to them and assess its reliability and relevance.
Algorithmic literacy holds immense implications for education in the digital age. As students navigate online platforms for learning, it's essential to equip them with the skills to critically evaluate the content they encounter. Incorporating algorithmic literacy into educational curricula empowers students to discern between credible and misleading information, fostering a culture of digital literacy and responsible citizenship.
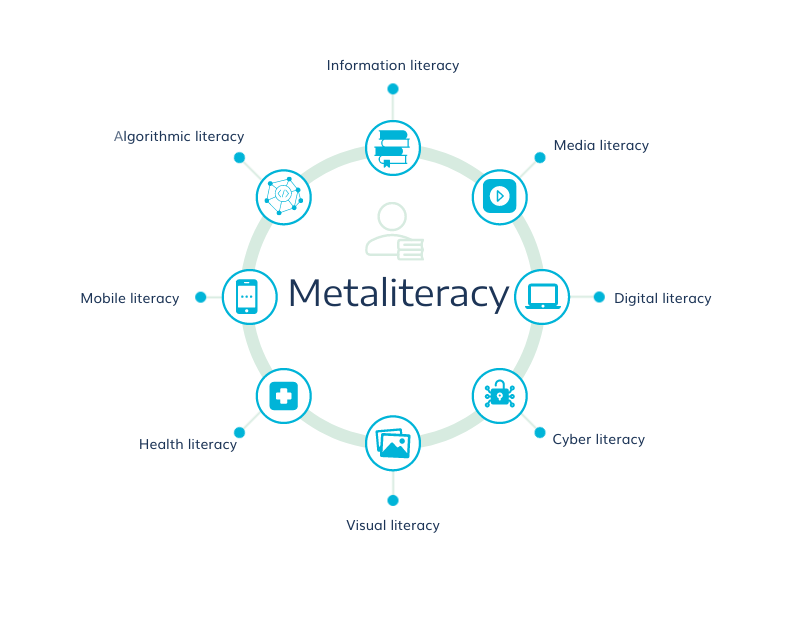 |
| Many authors see algorithm literacy as part of a broader set of skills called metaliteracy. (📷 bccampus) |
However, algorithmic literacy also presents challenges and ethical considerations. The opacity of many algorithms, often referred to as the "black box" phenomenon, raises concerns about transparency and accountability. Without insight into how algorithms operate and the biases they may encode, individuals risk being subjected to unintended consequences, such as algorithmic discrimination or filter bubbles.
To address these challenges, efforts to promote algorithmic literacy must be multi-faceted. Educational institutions, policymakers, and technology companies all play a role in fostering algorithmic literacy among the general public. Initiatives such as workshops, online resources, and educational campaigns can empower individuals to navigate the digital landscape with confidence and discernment.
 |
| Without algorithmic literacy users face unintended consequences. (📷 canva) |
Algorithmic literacy is a critical skill for thriving in the digital age. By understanding how algorithms shape our online experiences and learning to navigate them effectively, individuals can harness the power of technology for positive change. As we strive for a more informed, empowered, and equitable digital society, algorithmic literacy serves as a cornerstone for progress and digital wellness.
⭐⭐⭐
*AI assisted
Comments